How to Value Your First Stock In 1 Hour or Less - No Finance Knowledge Required!

In this article, you'll use the beginner-friendly “PE Ratio Comparison” technique to value a bank.
This article will be split into 2 parts:
- The Basics - Where I'll discuss some background about the PE Ratio Comparison technique.
- Application - Where you'll follow along as we value a company with PE Ratio Comparison.
The Basics
About P/E Ratios
“PE” stands for Price/Earnings. To get the PE Ratio of a company, divide its stock price by its per-share earnings.
P/E Ratio = (Current Stock Price) divided by (Earnings Per Share for the Last 12 Months)
Here’s an example. You’re given this data:
- Company X’s profit last year = 100 pesos per share
- Current stock price of Company X = 1000 pesos
What is Company X’s P/E ratio?
If you guessed that its P/E ratio is 10, you’d be correct!
Here’s the calculation:
P/E Ratio of Company X = Price / Earnings
= (1000 pesos per-share market price) / (100 pesos per-share earnings)
= 10
A P/E ratio of 10 means that the market is willing to pay 10 pesos for every 1 peso of Company X’s earnings last year.
How “PE Ratio Comparison” works
In general, companies with low P/E ratios are considered “cheap”, while those with high P/E ratios are more “expensive”.
A P/E ratio of 5 is “cheaper” than a P/E ratio of 10. 1 peso of the P/E=5 company's latest annual profit only costs 5 pesos, while for the latter, it costs 10 pesos.
PE Ratio Comparison assumes that similar companies tend to get similar P/E ratios. We can therefore use the average P/E ratio of a group to see if any of its component companies are "cheaper" or "more expensive" than the average.
Here's a quick example:
- You have a real estate company - Company Z
- Its stock price is 10 pesos per share
- Its profits last year were 2 pesos per share.
- This means Company Z has a current P/E ratio of 5.
- The calculation: Price/Earnings = 10/2 = 5.
- Let's say that the average P/E ratio for most real estate companies is 10.
- Therefore, the valuation for Company Z will be 20 pesos per share
- The calculation: Earnings*Industry P/E = 2*10 = 20.
Based on our example, Company Z looks like a good buy. We can purchase it for 10 pesos per share and get 20 pesos of value: A 100% upside.
The Steps
Here's a broad overview of the steps we'll use for this analysis:
- Choose a target company to value
- Get a group of similar companies to your target company
- Get every company's P/E ratio
- Calculate the average P/E ratio of the whole group of companies
- Calculate the fair value using the group's average P/E
Application of PE Ratio Comparison
Step 1: Choose a target company to value
For this example, let's find the fair value of EastWest Bank (PSE: EW)
Step 2: Get a group of similar companies to your target company
Here are some other banks in the Philippine stock market for our PE Ratio Comparison:
- Asia United Bank (PSE: AUB)
- China Banking Corporation (PSE: CHIB)
- Philippine Bank of Communications (PSE: PBC)
- Philippine Business Bank (PSE: PBB)
- Union Bank of the Philippines (PSE: UBP)
- Rizal Commercial Banking Corporation (PSE: RCB)
- Metropolitan Bank & Trust Company (PSE: MBT)
- Bank of the Philippine Islands (PSE: BPI)
- BDO Unibank, Inc. (PSE: BDO)
You don't have to list every company in an industry. However, the more companies you can compare with, the better.
Step 3: Get every company's P/E ratio (including the target company, EastWest Bank)
For this step, I'll show you how to get BDO's P/E ratio.
I’ll be using company annual reports as data sources. While sites like Yahoo and Marketwatch are more user-friendly, their earnings data tend to be inaccurate.
I recommend going through these steps yourself. Practice builds confidence.
3a. Get the latest annual earnings.
- Go to the company website and look for "Investor Relations", “Disclosures”, or similar sections.
- Look for the SEC filings. For the Philippines, the annual reports are called "17-A"'s, while in the USA, the annual reports are called "10-K"'s. Download the latest one.
If you're doing your calculations mid-year, use the last four quarters' earnings. This ensures your calculations are up to date. For the sake of simplicity, we will be using annual earnings data here instead of quarterly.
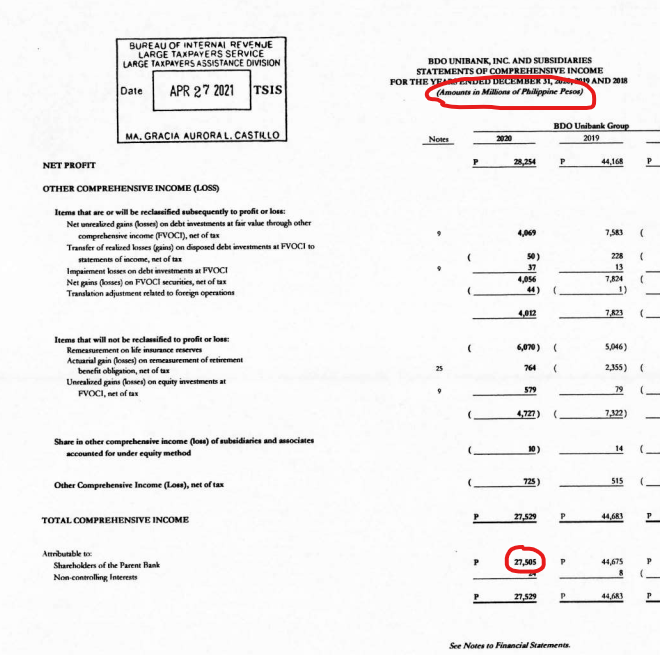
3b. Get the earnings from the annual report in the income statement.
In the 17-A annual report, look for the income statement and scroll to its last few lines, where you'll find "Total comprehensive income".
If there's an item under total comprehensive income that sounds like "Attributable to shareholders of the company", that's the earnings you'll use. Otherwise, just use total comprehensive income.
Here's how we did it for BDO:
- Scroll to the income statement of their 2020 17-A annual report.
- Note that their income statement is in millions of pesos.
- Note the line for comprehensive income attributable to shareholders - it's 27,505.
- Therefore, BDO's earnings for 2020 was 27,505 million pesos.
3c. Find the shares outstanding
You can use Bloomberg, WSJ, and similar websites for this step. Find the page for your company and get the "Shares Outstanding".
Here is BDO’s WSJ page: https://www.wsj.com/market-data/quotes/ph/bdo
At the time of writing, their shares outstanding is around 4.38 billion.
3d. Calculate the earnings per share
Divide the profits from step 2 by the shares outstanding from step 3.
For BDO, recall that:
- Earnings was 27,505 million for 2020.
- Shares outstanding is currently 4.38 billion.
Therefore:
Profits per Share = Earnings / Shares Outstanding
= 27,505 million / 4.38 billion
= 6.38 earnings per share
3e. Calculate the P/E ratio
Now that we have the "Earnings" for the P/E ratio, let's get the price.
For BDO, a quick google search tells us it's currently at 104.1 per share as I write this.
So now we know the following:
- Price is 104.1 per share
- Earnings is 6.38 per share
We can now calculate BDO's P/E ratio:
Price / Earnings = 104.1 / 6.38
= 16.32
Congratulations - you just calculated your first P/E ratio!
3f. All company P/E ratios
I’ve calculated the rest of the P/E ratios using the method above. Here are the results:

Note that BDO's P/E ratio differs here because I used the exact "shares outstanding" value here. The previous calculation used a rounded estimate.
Step 4: Calculate the average P/E ratio
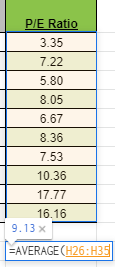
The average P/E ratio of banks in the Philippines at the moment is 9.13.
Step 5: Calculate the fair value using the group average P/E
To calculate the fair value of EastWest Bank (PSE:EW), multiply its profit per share by the group average P/E ratio.
Remember:
- EW's profit per share is 2.85.
- The average P/E of Philippine banks in our analysis is 9.13.
Here's the calculation:
Fair Value = Profit Per Share * Group Average P/E
= 2.85 * 9.13
= 26.02 pesos per share.
According to our calculation, we can purchase EW shares for 9.56 pesos at the moment and get 26.02 pesos of value. You'll still need to do further research to identify whether this is a good purchase, but this result tells us that it might be worth spending the time to look deeper into EW.
For comparing companies, you can calculate the upside of the fair value versus the current price. Here's the calculation for EW:
% Upside = (Fair Value / Current Price) - 1
% Upside of EW = (EW's Fair Value / EW's Current Price) - 1
= (26.02 / 9.56) - 1
= 172.3% upside from purchasing EW
Valuing All Group Members
Notice that we have all the data needed to value every company in our group of Philippine banks.
Just apply the same calculations to the other companies, and we'll get the following results:
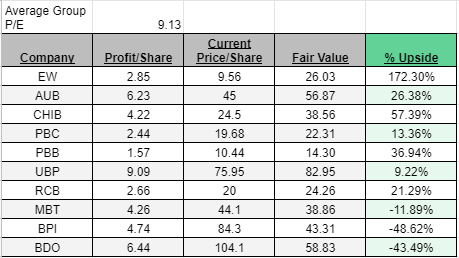
Your first valuation
Congratulations - you've just finished your first stock valuation.
PE Ratio Comparison is easy but not comprehensive. Sometimes stocks are cheap for a reason, so you need to augment this tool with further research.
However, I hope this first valuation has given you the confidence to press on and try learning more ways to analyze companies yourself.